Amazon Inspector
Another tool an IT auditor can leverage in AWS is Amazon Inspector. Amazon Inspector is an automated vulnerability management service that continually scans AWS resources for software vulnerabilities and inadvertent network exposure.
Amazon Inspector collects events from various vulnerability intelligence sources, including Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), and MITRE. To get to Amazon Inspector, you can search for it on a browser or the AWS console, as seen in Figure 7.11:

Figure 7.11 – Amazon Inspector
You need to enable Amazon Inspector to facilitate the discovery of data, as seen in Figure 7.12:

Figure 7.12 – Enabling Amazon Inspector
Navigate to the Dashboard tab on Amazon Inspector and you will find information such as Critical findings and Risk based remediations:
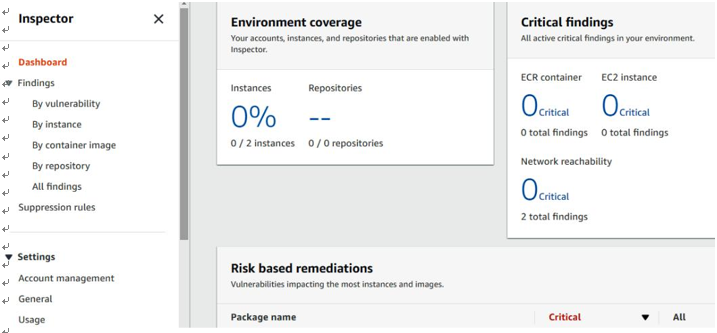
Figure 7.13 – The Amazon Inspector dashboard
One useful tab in Inspector is Findings. In our example, there are two findings noted: ports 22 and 3389 are reachable from an internet gateway. Ports 22 and 3389 are Secure Shell (SSH) and Remote Desktop (RDP), respectively. If you can recall from Chapter 4, Network, Infrastructure, and Security Controls, we noted that Azure CIS Benchmarks recommends that clouds should not allow unrestricted access to remote server administration ports, such as SSH to port 22 and RDP to port 3389. Exposing SSH and RDP to the internet can increase opportunities for malicious activities, such as brute-force attacks.
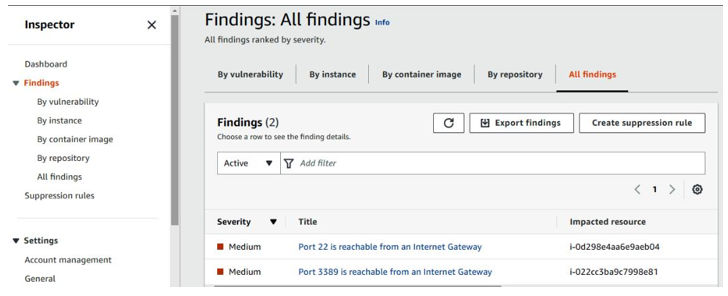
Figure 7.14 – The Amazon Inspector findings
In addition, Amazon Inspector has integration with Amazon EventBridge and AWS Security Hub.
You can see this integration with AWS Security Hub in Figure 7.15:
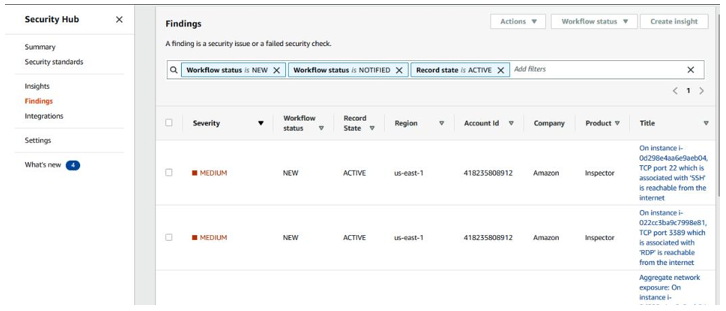
Figure 7.15 – Integration with AWS Security Hub
Next, we will look at tools in the Azure cloud environment.
Azure
Now, we will review cloud auditing tools that can be leveraged in the Azure cloud platform.
Azure Monitor
One tool an IT auditor can leverage in the Azure environment is Azure Monitor. As per the Azure documentation, Azure Monitor “helps you maximize performance and availability of your applications and proactively identify problems in seconds.”
To launch Azure Monitor, you can easily search for it in a browser or on the Azure console, as seen in Figure 7.16:
Figure 7.16 – Azure Monitor
Overview presents the different options that an IT auditor can utilize from Application Insights,Container Insights, VM Insights, and Network Insights, as seen in Figure 7.17:
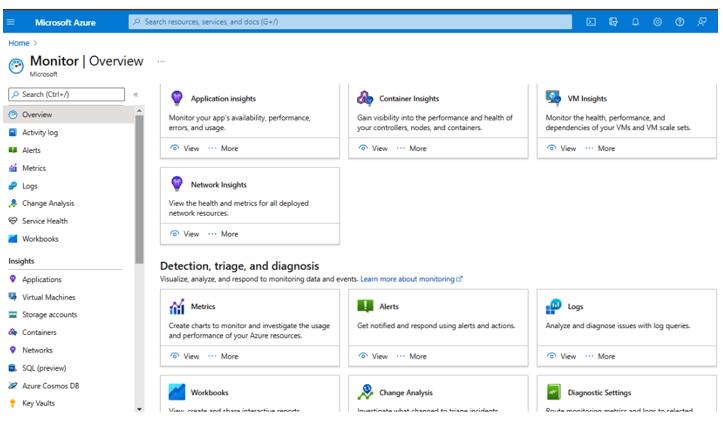
Figure 7.17 – Azure Monitor Overview
A useful feature of Azure Monitor is Activity Log, which displays the last transactions executed in the Azure cloud and who initiated the transaction, as seen in Figure 7.18:
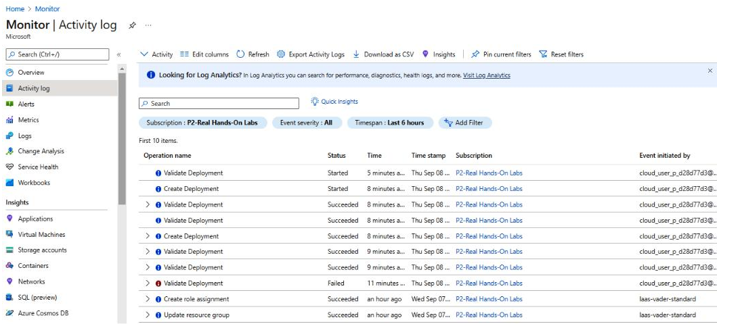
Figure 7.18 – Azure Monitor Activity log
This can be useful to an IT auditor who needs to document who performed a certain transaction.
Another feature that can be useful to an IT auditor is Alerts. You can set up alerts for various conditions. In this example, we are setting up alerts for All Administrative operations over the last week, as seen in Figure 7.19. This type of rule can be useful to an IT auditor when monitoring administrative operations and ensuring they are authorized.
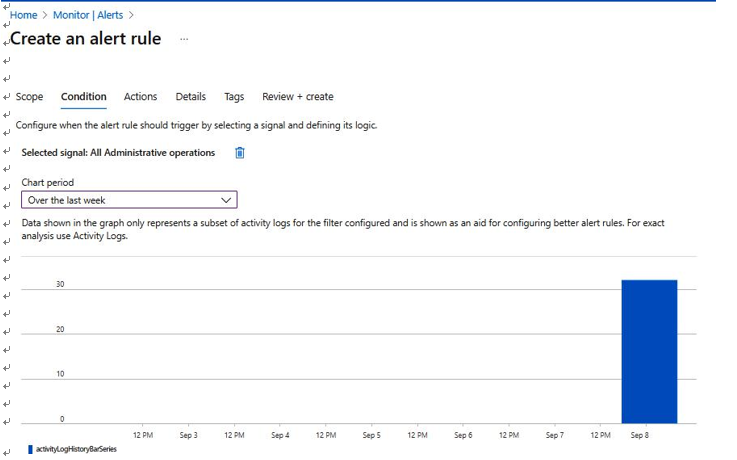
Figure 7.19 – Creating an alert rule
Next, we will look at another Azure tool, referred to as Azure Network Watcher.