AWS Trusted Advisor
AWS Trusted Advisor provides real-time best practice guidance to help provision, monitor, and maintain AWS resources. You can then follow AWS Trusted Advisor recommendations to optimize your services and resources. These best practice recommendations span five categories:
- Cost optimization
- Performance
- Security
- Fault tolerance
- Service limits
To launch AWS Trusted Advisor, search for the service in the AWS console, as seen in Figure 6.16:
Figure 6.16 – Searching for AWS Trusted Advisor
The following screenshot is from AWS documentation and shows an example of the AWS Trusted Advisor interface, as seen in Figure 6.17:

Figure 6.17 – The AWS Trusted Advisor interface
Azure
A core tool an IT auditor should leverage in the Azure environment is Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defenderfor Cloud (formerly known as Azure Security Center) is Azure’s native solution. The service helps measure, maintain, and improve the level of security by continuously assessing resources and providing recommendations. You can use Microsoft Defender to determine the population of cloud resources. To launch Microsoft Defender, search for it in the search bar. TheOverview tab has information such as Security posture, Azure Subscriptions, and Active Recommendations, as seen in Figure 6.18:
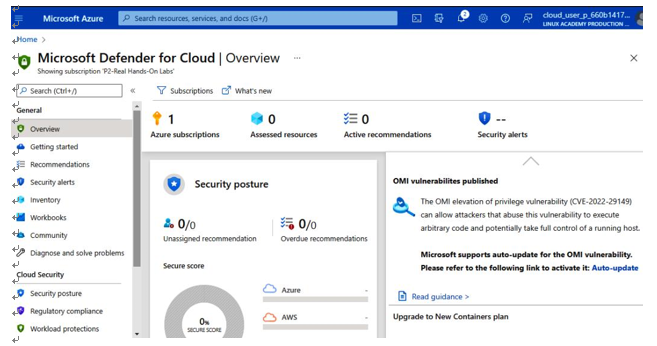
Figure 6.18 – The Overview tab
The Inventory tab displays the total resources running in Azure. It gives information such as resource type and health status, as seen in Figure 6.19:
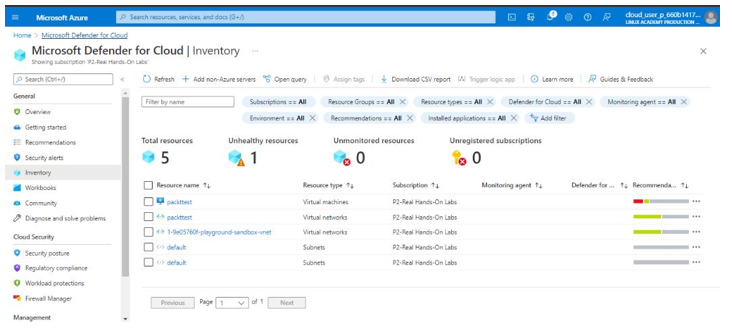
Figure 6.19 – The Inventory tab
In our example, we have 1 unhealthy resource. The auditor would need to investigate this resource further.
The Recommendations tab provides Azure recommendations with related severity of issues. As you can see in our example, we have wide open network ports and Microsoft Defender recommends we should restrict them:
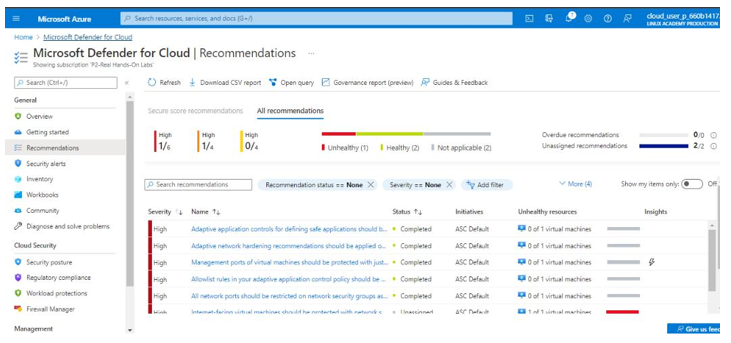
Figure 6.20 – The Recommendations tab
Under the Cloud Security section is Security posture, which provides a holistic view and a secure score as seen in Figure 6.21:
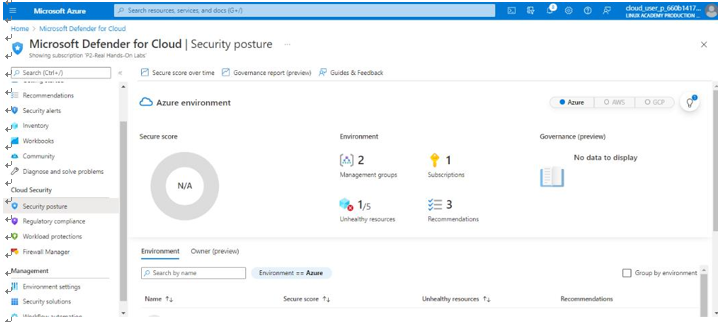
Figure 6.21 – The Security posture tab
Another item under the Cloud Security section is Regulatory compliance. In this section, you can add and track customized regulations that you want your organizations to align with, as seen in Figure 6.22:
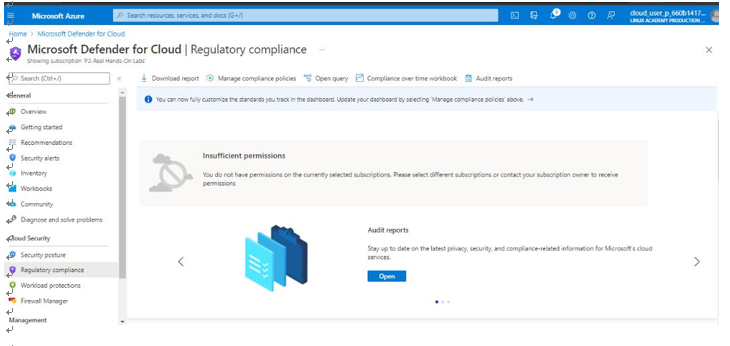
Figure 6.22 – Regulatory compliance
Another tool an IT auditor can leverage is Microsoft Purview.
Microsoft Purview
Microsoft Purview (formerlyAzure Purview) is a centralized data governance and risk management service that helps manage data. To set up Microsoft Purview, you can search for it on any browser,
or go to https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/purview/#overview, as seen in Figure 6.23:
Figure 6.23 – Azure Purview
You will need to set up a Microsoft Purview account, as shown inFigure 6.24:
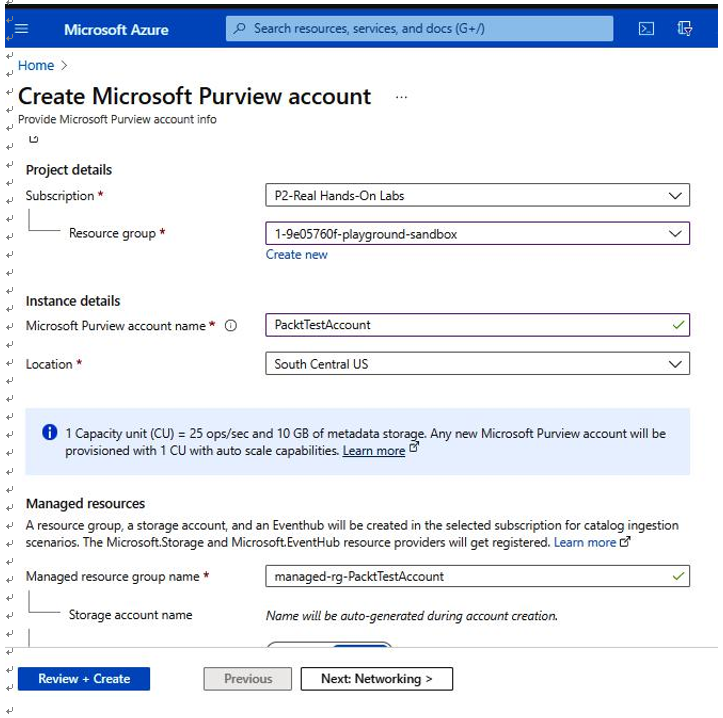
Figure 6.24 – Creating the Microsoft Purview account
With the account created, launch the Microsoft Purview workspace from the Azure portal, as shown in Figure 6.25.
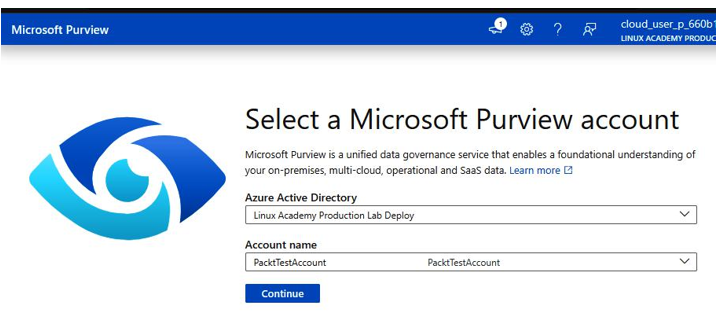
Figure 6.25 – Selecting an account
With Microsoft Purview launched, you are able to navigate to theBrowse assets and Manage glossary tabs, as seen in Figure 6.26:
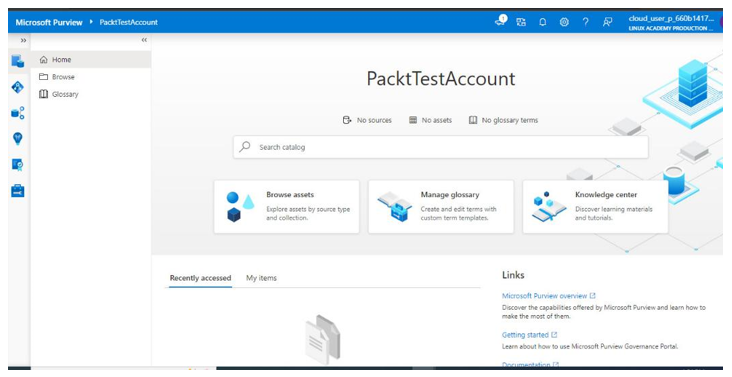
Figure 6.26 – Microsoft Purview Home page
If you click on Browse assets, it displays the population discovered, as seen in Figure 6.27.
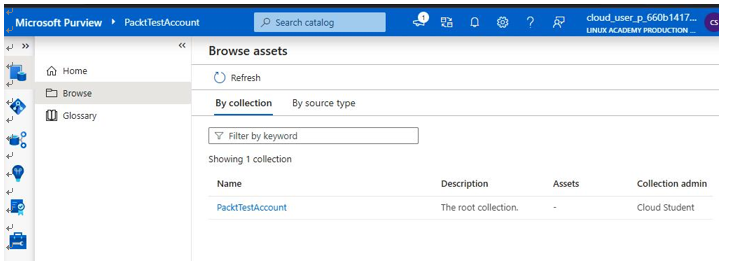
Figure 6.27 – Browse assets
Before Microsoft Purview scans your data, Microsoft Purview will need to be given access to data sources. You can do this by assigning Microsoft Purview managed identity access rights.
Once configured, Purview can create a holistic, up-to-date map of your data landscape with automated data discovery, sensitive data classification, and many other data insights, as shown in Figure 6.28:
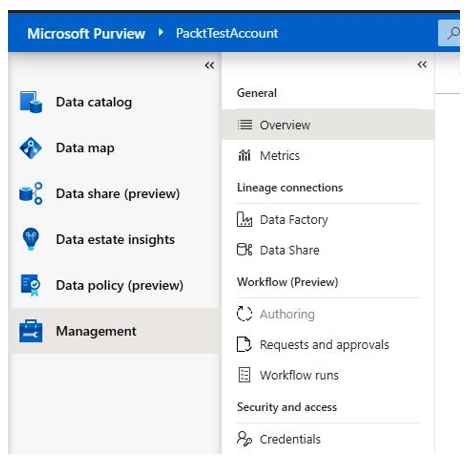
Figure 6.28 – Management | Overview
GCP
IT auditors can leverage a tool called Security Command Center for GCP.